One of the pillars of SEO is to provide relevant information to visitors. Therefore, SEO experts want to keep updating the content and technology of the pages displayed on the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) using redirects to keep up with the latest trends.
As a result, many pages become obsolete at some point and no longer accept changes. In these cases, we’ll need to create a new page with much more optimized technology, for example, using the HTTPS Protocol or presenting a cleaner URL.
This sounds pretty logical and easy but. However, it takes effort because it involves a lot of analysis and work to pass the information on to another. Let’s dig a little deeper into this topic.
Table of Contents
What is an SEO redirect?
A redirect is an HTTP Status code assigned to the current/old page, which tells Google to display the newer one instead. So basically, you add a redirect into your webserver to indicate the new URL that will replace the old one. Then, search engines display the more recent page on the visitor’s browser instead of the old one.
Essentially, it automatically directs visitors to another page without them even noticing; well, it shouldn’t be noticeable, but we’ll talk about that later. To sum up: the same website will send both visitors and search engines to a different URL than the one users either typed in on their browser or picked from the Google results.
Why should I redirect a URL?
There are several scenarios in which we require redirects. Schematically, we can highlight the following situations:
- Moving your site to a new domain.
- Consolidating two websites into one.
- Restructuring the entire website architecture.
- Dealing with old pages that are no longer needed but have a decent amount of traffic.
- You have a product page where the product is no longer available.
- You migrate from HTTP to HTTPS.
Types of redirects
There are several different redirect possibilities. Let’s look at the most common redirects for SEO and understand their characteristics.
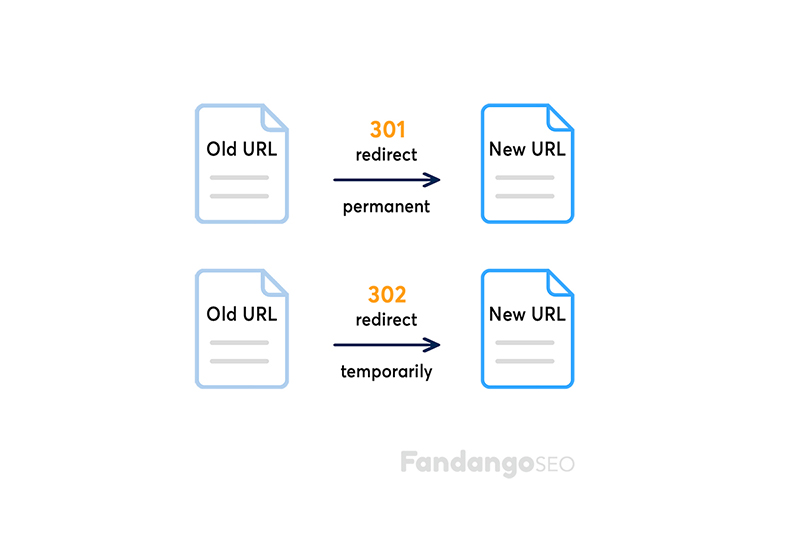
What is a 301 redirect?
You want to use this one when the page you redirect to is the final version you wish to show on search engines. A 301 redirect is permanent and will be considered by Google and other search engines.
From an SEO point of view, a 301 redirect passes link equity (also known as link authority or link juice) to the redirected pages. Therefore, assigning a 301 status code to an old post with good page authority is a common practice in SEO.
What is a 302 redirect?
Now that we know how the 301 redirect works, it’s difficult to believe there are other types because that one makes a lot of sense. But many pages require temporary URLs, for example:
- Special promotions that expire soon.
- When a webmaster wants the home page to display a clean URL, but the real version is long (and ugly), even though it has A LOT of authority. The solution is to add a 302 redirect to show a nice URL, which people will feel like sharing, but still index the older –and more powerful- one.
- When you temporarily need to host a page somewhere else, knowing that the final location will be the original one.
In these cases, we’ll want to redirect users using a 302 temporarily, but we still wish search engines to crawl the original page.
Other types
A 307 redirect is another temporary redirect, but it isn’t relevant to your SEO strategy or Meta Refresh. So try to stick to 301 or 302 redirects.
How to 301 redirect
In Search Engine Optimization, any major action starts with a comprehensive analysis. Here is a list of elements you need to bear in mind before redirecting a page:
- Look for the incoming links to the page, both internal (from the same website) and external (from other websites). You want to point the internal ones to the newer page and update the external incoming links to maintain the site authority.
- You’ll want to check the outlinks (the links of the page that point to your site) and the outbound links (the ones you send to other websites). Remember that some pages rely on the link juice this page is sending them. 😉
- Check the canonicals. You don’t want to point to a page that’s being redirected. Readjust this HTML tag on the pages that have a canonical pointing to this page.
- Once you’ve done all this analysis and have rearranged the links and canonicals, you can start implementing the 301. Don’t make any changes before being sure you’ll send the same link juice to the newer page.
- Run a crawl to check that you have implemented all the elements correctly.
- Redo the XML Sitemaps and upload the new list to Google Search Console.
Remember that FandangoSEO can help you speed up this whole process by assisting you during the analysis, testing of new pages, and generating XML sitemaps.
You can also find more SEO tips on our blog post on how to implement redirects correctly.
How do I redirect a website?
Apart from following the previous guide, don’t forget to use these tips to redirect a website:
- Don’t move to a new domain before setting all the 301 redirects. You don’t want Google to crawl a website with no inlinks and duplicate content, right?
- Set 301 redirects between http:// and the http://www versions of your domain. This is something we often forget, but it’s a must in SEO.
- Avoid redirect chains (we’ll talk about them later).
- You can also use Google Search Console to tell Google that an entire domain has now changed to another one.
- Notice that this is a brand-new page to Google, so it will take some time for it to rank as high as the old one. That’s why it is so important to plan your SEO strategy for successful website migration.
Are redirects bad for SEO?
One of the most frequently asked questions about this subject is “Do redirects hurt SEO?.” When exploring the site, redirects aren’t the best response code you can show Google, but they are necessary in many cases. So, redirects aren’t bad for SEO unless (there’s always an “unless”) you are not aplying them the right way.
One 301 redirect increases the page loading time. The users don’t usually notice that. However, it’s taken into account by Google, as it takes an extra step for the spider to crawl the newer page, which can add some milliseconds to the loading speed.
Now, suppose you have a redirect between page A and page B and decided to create a page C sending a newer URL redirection on top of the existing one. That would be two redirects from page A for the bot to follow. Is that negative? Yes.
Then, is there a limit to the number of redirects on a website? Nope, but there is a maximum number of redirects per one page. Google recommends not to exceed 2 in a row. 5 or 6 would be too many already, and the spider would stop visiting the site. This so-called redirect chain means that for each extra page, the user experiences a delay and consequently loses interest, and so does the spider, meaning a page loses authority with redirect chains.
Matt Cutts explains this very clearly in a –fairly old- video which is still relevant to answer this question:
We firmly recommend ALWAYS redirecting to the latest page. Regardless of how much effort this will take you, it’s the only way not to increase the loading time and to avoid authority loss.
Redirect chain example:
URL1 redirects to URL2 redirects to URL3 to URL4 to URL5 (Final URL)
What a mess, right?
How you should solve it:
URL1 to URL5 (change the redirect to the latest URL)
URL2 to URL5 (same)
URL3 to URL5 (same)
URL4 to URL5 (This one is obvious 😉 )
Use FandangoSEO as a redirect chain checker to detect these issues and assist you with website migrations.
Using a redirect checker
Now that you have a good understanding of redirects in SEO and how to use them correctly so they do not hurt SEO, you should know how to review them. The quickest way is by using a redirect checker like FandangoSEO. It is a powerful SEO crawler that provides you with a list of all your redirect URLs with its status code so you can quickly fix any issue.
As discussed, redirecting websites takes a lot of time and effort, but you’ve also invested a lot in generating the newest page, and you want visitors and search engines to find it smoothly, right? With that being said, dig into your data and invest all your resources in implementing an optimal 301 redirect strategy.
